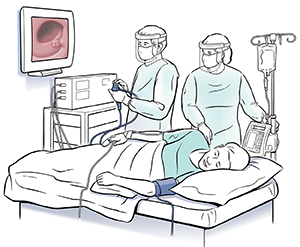
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is a procedure used to look inside the lower colon (also called sigmoid colon), descending colon, and rectum. This test can help find the source of belly pain or rectal bleeding. It can help find the reason for changes in bowel habits and unexplained weight loss. It's used as part of the screening for colorectal cancer. It's done using a sigmoidoscope. This is a flexible, narrow tube. The tube has a light and a small video camera on the end. Flexible sigmoidoscopy can show irritated or swollen tissue, ulcers, polyps, and cancer.
Screening
The American Cancer Society and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force advise that you start having regular screening for colorectal cancer if you’re 45 or older and at average risk. Screening may find diseases at an early stage. A sigmoidoscopy is advised every 5 years. Your doctor may also advise other colon cancer screening methods. These include colonoscopy. Talk with your doctor about colorectal screening. If a sigmoidoscopy shows polyps, you may need a colonoscopy as the next step. It can examine the rest of your colon.
Getting ready
To get ready for the test:
Tell your doctor about every prescription and over-the counter medicine you take. This includes vitamins, minerals, and any other supplements you use.
Tell them about any health conditions you may have. Tell them if you've had a recent illness, such as an infection.
Ask your doctor about the risks of the test. These include bleeding and bowel puncture.
Your rectum and colon must be empty for the test. Follow the diet and bowel prep directions from your doctor. There should bet little or no stool in your intestine. Otherwise, the test may need to be rescheduled.
The bowel prep will cause diarrhea. Stay close to a bathroom. A complete bowel prep results in clear and liquid stool.
Your doctor will tell you to follow a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure.
You will be asked to sign a consent form. Make sure all of your questions are answered before you sign.
During the test
Here is what to expect:
Your doctor will tell you how long before the procedure you should have nothing by mouth.
The test may be done in the doctor's office. Or it may be done in an outpatient surgery center or in a hospital. You may wear a gown or a drape over your lower body.
It usually takes
10 to 20 minutes.Most people aren't sedated for this procedure. But if you are very anxious about it, talk to your doctor. Discuss the pros and cons of sedation.
The doctor does a finger (digital) rectal exam. This is to check for anal and rectal problems.
The rectum is lubricated. Then the scope is put in.
You may feel like you need to have a bowel movement. You may feel pressure when air is pumped into the colon. This is done so that the doctor can get a better view. It’s normal to pass gas during the test.
The camera sends a video image of your intestinal lining to a monitor. This helps the doctor see the tissues lining your sigmoid colon and rectum.
During the procedure, your doctor may remove colon polyps. They will be sent to a lab for testing. Colon polyps are common in adults. They are harmless in most cases.
If your doctor sees abnormal-looking tissue in your colon, they will take small tissue samples. This is called a biopsy.
After the test
Here is what to expect:
Your doctor will likely talk with you about the results right away. This might not happen if you’re having other tests.
If a biopsy was done, ask when to call for the results.
Try to pass all the gas right after the test. If you don't, you may have bloating and cramping.
Slight bleeding from the rectum is normal. This can happen if a biopsy is done.
After the test, you can go back to your normal diet and other activities.
When to call your doctor
Contact your doctor right away if you have:
Severe pain in your belly.
A fever.
Lasting bloody bowel movements.
Dizziness or weakness.
A lot of rectal bleeding.
Symptoms from the procedure that get worse.
New symptoms.