What Is Atrial Flutter/Atrial Fibrillation?
The heart has its own electrical system. This system makes the signals that start each heartbeat. The heartbeat begins in 1 of the 2 upper chambers of the heart (atria). A problem can make the atria beat faster than normal. The atria may beat fast but still evenly. This problem is called atrial flutter. If the atria beat very fast and also unevenly, it is called atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Causes of Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation
Causes of these problems can include:
-
Previous heart attack
-
High blood pressure
-
Thyroid problems
In many cases, the cause is unknown.
When the Atria Beat Too Fast
The atria may beat fast only once in a while. This is called a paroxysmal heart rhythm problem. If they beat fast all the time, it is a chronic problem.
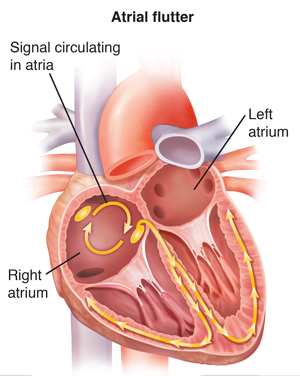
Atrial Flutter
With atrial flutter, electrical signals travel around and around inside the atria. These circling signals make the atria beat too fast:
-
Atrial flutter can cause symptoms similar to AFib. It can also lead to the even faster, uneven rhythms of AFib.
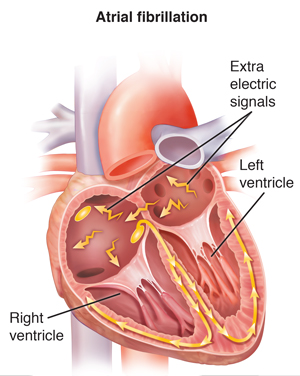
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
With AFib, cells in the atria send extra electrical signals. These extra signals make the atria beat very fast. They also beat unevenly:
-
The atria beat so fast and unevenly that they may quiver instead of contracting. If the atria don’t contract, they don’t move enough blood into the 2 lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). This can cause you to feel dizzy or weak.
-
Blood that doesn’t keep moving can pool and form clots in the atria. These clots can move into other parts of the body and cause serious problems such as a stroke.
Symptoms of Atrial Flutter and AFib
These symptoms include the following:
-
Palpitations (a fluttering, fast heartbeat)
-
Weakness or tiredness
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain or tightness
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Fainting spells